Security researchers at Microsoft have discovered several vulnerabilities in Linux System. The vulnerabilities collectively referred to as Nimbuspwn, could allow an attacker to elevate privileges to root on many Linux desktop endpoints. These vulnerabilities allow to deploy payloads, like a root backdoor and perform other malicious actions via arbitrary root code execution.
The vulnerabilities are referred to as CVE-2022-29799 and CVE-2022-29800. The vulnerabilities are rooted in a systemd component called networkd-dispatcher, a daemon program for the network manager system service that’s designed to dispatch network status changes.
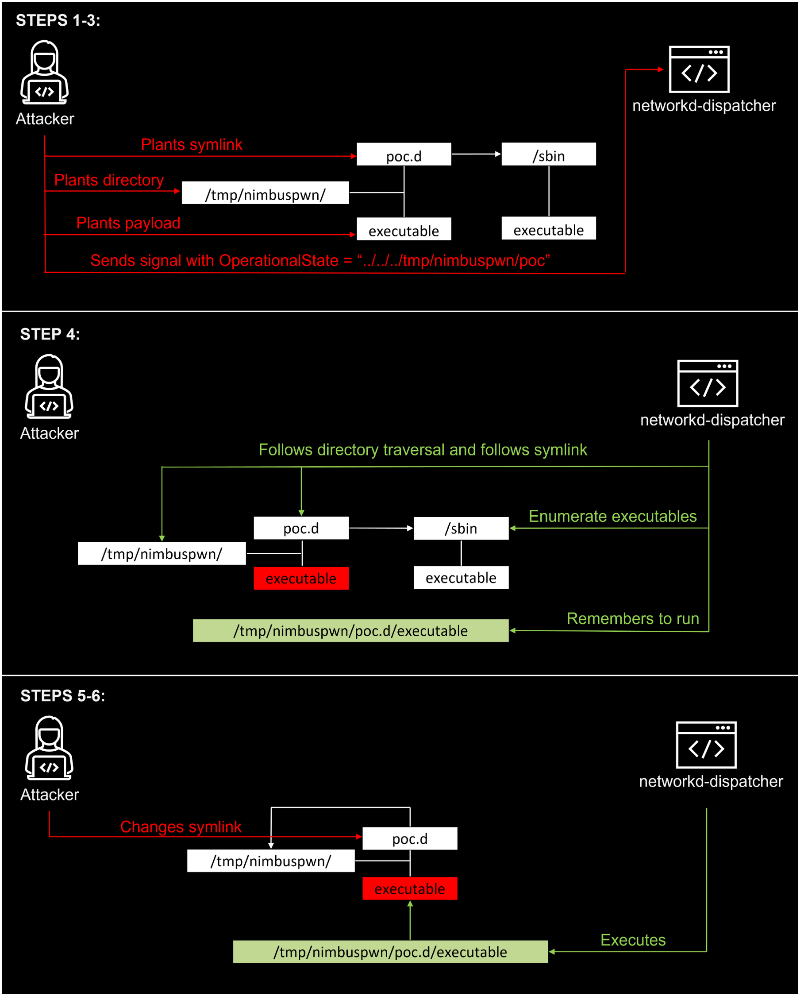
The goal of networkd-dispatcher is to dispatch network status changes and optionally perform different scripts based on the new status. It runs on boot as a root. There is a certain time between the scripts being discovered and them being run. An attacker can abuse this vulnerability to replace scripts that networkd-dispatcher believes to be owned by root with ones that are not.
To ensure Linux executes the attacker-supplied malicious script rather than the legitimate one, the attackers can plant multiple scripts until one finally succeeds. Microsoft researchers shared a proof-of-concept where they highlighted that in three attempts, they were able to successfully plant their files.
Fixes for these vulnerabilities have been successfully deployed by the maintainer of the networkd-dispatcher, Clayton Craft. Users will be able to find the new version in a systemd update on their Linux machines. Otherwise, they can deploy the patches by manually installing the latest network-dispatcher build.